Imagine waking up in the morning and reaching for your phone, but when you hold the camera up to your face, it doesn’t unlock. It’s been ages since you’ve used your passcode, but after several failed attempts, it comes back to you.
You open your social media app of choice. What it displays is…not relevant? Yeah, it’s definitely not relevant: it’s a bunch of stories you don’t care about from friends you haven’t spoken to in years.
“Okay, Google,” you call out to your Google Assistant. “Is Instagram down?”
But there’s no response.
You’re thirty seconds into your day, but already, life feels different. Why?
Welcome to your life without AI.
So often we think of AI as being that futuristic, far-off thing that’s depicted in the movies in the form of humanoid robots that are good, bad, or in that complicated gray area in between (we’re looking at you, HAL from 2001: Space Odyssey).
The fact is, AI is not only here, but it’s also already integrated into our everyday lives. It just looks and acts quite a bit different than what we’re used to seeing on TV. If we were to lose that AI tomorrow, well – our lives would look quite different! Here are a few ways things would change.
Voice-powered assistants wouldn’t be so helpful

Photo credit: BENCE BOROS on Unsplash
“Hey, Google. What’s a trendy Chinese restaurant near me for date night…maybe Szechuan…or umm…Thai?”
“Here are results for twenty Chinese restaurants…”
From Amazon’s Alexa to Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant, and Microsoft’s Cortana, AI-powered voice assistants have made their way into many of our homes, onto our wrists, and into our smartphones. All you have to do is talk and they respond instantly.
In order to do this, voice-powered assistants must understand language and make a decision about what to suggest or how to act. Language processing is something no animal other than humans can do to the complexity, depth, and degree that we do it – and it’s a capability that took us thousands if not millions of years to develop (there’s much debate in the scientific community about what can be considered the first roots of language, and whether it began in our genus or further back).
Understanding and acting on human language input is a capability that still challenges computers, but thanks to AI algorithms using natural language processing and machine learning, they’re expanding all the time.
So if you check the weather, play the music of your choice, schedule new events, or find a spicy new dinner spot near you simply by asking Siri, then AI is already an integral part of your life.
The drive to work would be boring and long
Photo credit: Jonas Leupe on Unsplash
Every time you use Google Maps to find your way in a new city or Waze to get you to work faster, you’re benefiting from AI. Google Maps and other mapping apps like it have long relied on historical data to analyze traffic patterns and predict commute times based on location and time of day. But it’s AI that helps predict what that route will look like in 10, 15, 20 minutes from now by making in-the-moment predictions based on analyses of live traffic patterns. This has proven all the more crucial in further improving accuracy over the past several years as traffic patterns have become more unreliable during pandemic shutdowns and re-openings.
And if you want to jam out to personally customized tunes on Spotify while you take the scenic route? Yep, you need AI for that too. Spotify uses natural language processing (NLP) to scan mentions of that track and artist across the internet to compile them into what the company calls “cultural vectors” and “top terms.” These are then weighted as a part of determining what songs to play you next.
And that’s just the start of Spotify’s use of machine learning. The platform also uses collaborative filtering, taking into account your behavior, including how many times you’ve played a song, clicked on an artist’s profile, saved a song to a list, or repeated a song. Finally, Spotify uses audio models and convolutional neural networks, the same technology used in facial recognition technology, to analyze and categorize raw audio tracks that you might be interested in.
It’d be hard to find anything on Google

Photo credit: Benjamin Dada on Unsplash
Every time you search for something in Google, imagine getting all the results listed in alphabetical order…instead of ordered by relevancy!
Google released RankBrain, its first foray into AI for search, in 2015. RankBrain operates in all languages and learns from search queries, matching phrases to concepts it’s found are related, and refining its abilities over time.
As of 2018, Google also began to use neural matching to understand how a particular query fits within the context of that page or query, which then becomes a part of the ranking algorithm.
Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), a neural network-based approach, arrived on the scene a year later to pre-train AI algorithms and help them better understand how different combinations of words express different meanings and intent. This was followed up in 2021 with the release of their Multitask Unified Model (MUM), which helps Google search algorithms not just understand but also generate languages, which is important for understanding variations in phrasing and languages.
Google still relies heavily on the non-AI-based search algorithms that it’s been developing since its creation, and in fact, there is a constant interplay between the two. Without AI, your Google search results would not be completely inaccurate…but there’d be a lot more misses and a lot of information overload, especially given the sheer volume of information that’s added to the internet across all languages on the globe every day.
Your finances would be at a greater risk

Photo credit: Clay Banks on Unsplash
In 2018, there were over one billion credit card transactions every day worldwide. In many places these days, you don’t even need to show your credit card — just tap your smartphone wallet and go.
Whereas in the past banks and credit card companies would try to detect fraud by setting up some hard rules (e.g. if you live in Houston, an attempted credit card purchase in San Francisco is rejected). If you lived through those times, you remember having to call your bank before traveling — or more embarrassingly, while standing at the checkout counter at the airport restaurant.
AI has vastly improved how accurately potential fraudulent activity can be detected. Using vast amounts of retail transaction data, account movement data, and purchasing behaviors, AI-powered fraud detection tools can establish a baseline for “normal” behavior on a per-person basis and use that to detect possible anomalous behaviors.
So now when you travel from Houston to San Francisco, you can go ahead and buy that Cinnabon at the airport and enjoy it without your bank calling you.
Recommendations would be irrelevant

Photo credit: David Pupaza on Unsplash
Meet up with friends, talk to colleagues around the (often virtual) water cooler, and you’ll frequently hear the phrase, “What are you watching?”
Head to Etsy or Amazon in search of a very specific product, and you’ll find exactly what you’re looking for in seconds.
And just try to scroll through Instagram (we dare you!) and not click on an ad perfectly tailored to exactly what you didn’t realize was missing in your life, but totally fixes all of your problems.
We’ve gotten used to being delivered hyper-relevant recommendations that suit our every last need, but it wasn’t too long ago when those recommendations were laughably bad. Launch Netflix and find yourself totally overwhelmed with movies you would never watch. Buy a mug on Amazon and then scroll through suggestions about dog leashes (???). Search for face masks on Etsy and get a bunch of Halloween masks.
No more.
Netflix’s AI algorithms use the metadata from media to make recommendations. AI creates teasers so you can quickly get previews. And AI plays a part in playback and content delivery, so the viewing experience is a smooth one.
Amazon relies on AI and machine learning to rapidly generate recommendations based on the data it analyzes. It builds models based on that data, then optimizes those models in real-time, building better, more relevant search results.
Etsy uses AI computer vision tools for search and product recommendations. These AI algorithms identify, tag, and create structured data for millions of unique SKUs, including those that are nearly a brand new concept in society.
Your doctor might miss something important
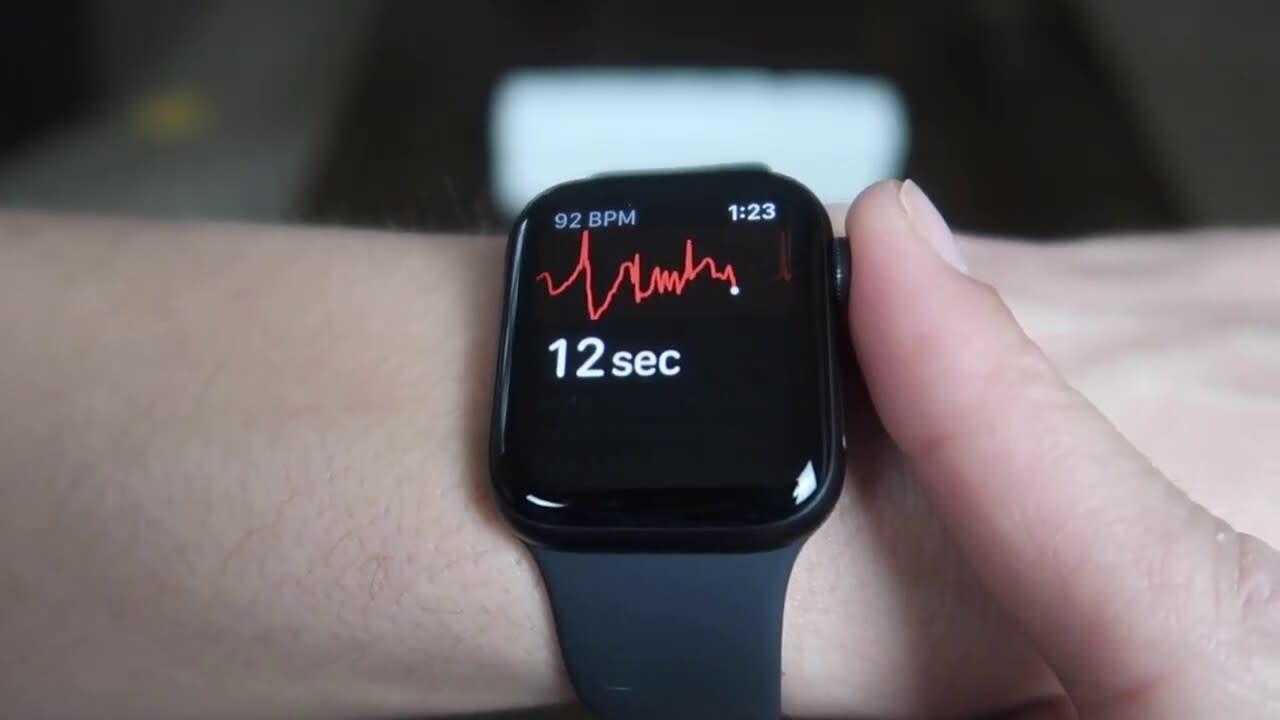

Photo credit: Apple
Not feeling too well? Could be the late night out last night…or the dinner…or something very serious that you need to get checked out. Once you go to your doctor, they might prescribe a blood test or an x-ray or some other diagnostics. A team of trained medical professionals pore through all this diagnostic data to find patterns and indicators for possible health issues…and they’re quite good at it.
Now AI can help them get even better results when analyzing such large amounts of data. Companies, like Athelas, use machine learning “to dramatically improve the speed and efficiency of testing blood cells.” AI has even proven to be able to detect breast cancer as well – and actually a bit better than – radiologists.
But what if your smartwatch could give you an early warning on possible health issues? The FDA-approved ECG functionality in the Apple Watch does just that. It uses artificial intelligence to detect AFib (atrial fibrillation) and other heart issues, though it should not be substituted for diagnostics under a doctor’s care.
Looks like the Apple Watch a day keeps the doctor away.
Your online orders would take forever + a day to arrive

Photo credit: Sticker Mule on Unsplash
…and they might be wrong when they get there. Covariant’s AI-powered robots are deployed in warehouses across the world to ensure the items you ordered online get to you as quickly as possible. These piece-picking robots automate previously manual tasks, with high speed and accuracy. Automation generally helps warehouses maintain a steady output during the ups and downs of order spikes (seasonal increases around the holidays and sales; shifting sales from in-store to online due to the pandemic) and retractions (economic slowdowns due to inflation, labor shortages, supply chain challenges, etc.). But getting traditional automation to function at a high level is challenging for many environments, such as in the apparel industry, where there’s a high volume of highly variable products.
What would your life look like without AI?
AI has been around for a mere sliver of the human timeline, so you might be thinking: meh, life without AI wouldn’t be so bad; we’ve done it before! True, but the Victorians didn’t have the internet, high-speed vehicles, social media, online shopping with access to almost every SKU that exists in the world, or the ability to search for a question from the most massive database of human knowledge that’s ever existed. Individual human minds simply aren’t built to process all of the information, data, and choice with which we’re constantly bombarded. Whether you’ve got a fully automated smart home or you simply use your phone to check the weather, every one of us engages with AI every day.
So load up Netflix, blast Spotify, drive with ease, and make good use of all of that real-world AI!
